Frontal Lobe
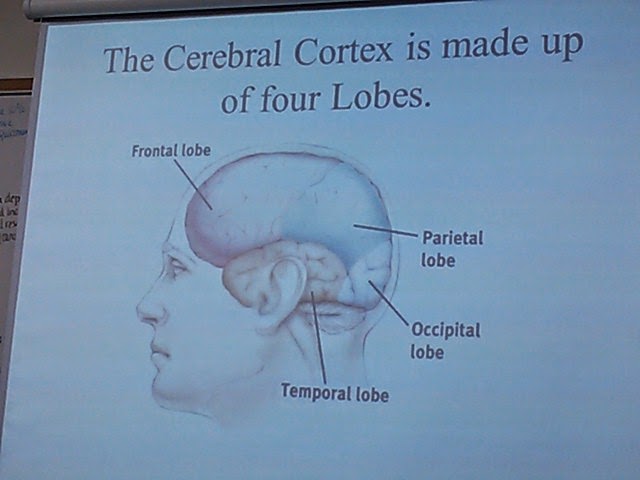 *Abstract thought emotional control
*Abstract thought emotional control*Containes Motor Cortex: sends signals to our body controlling muscle movements
*Broca's: Responsible for controlling muscles that porduce speech
* Damage to Broca's Area is called Broca's Aphasia: unable to make movments to talk
Parietal Lobes:
*Contain sensory cortex: receives incoming touch sensations from the rest of the body
* Most od the parietal lobes are made up of Association Areas
Assiociation Areas:
* any area not associated with receving sensory information of coordinating muscle movements.
Occipital Lobes
* deals with vision contains Visuals Cortex.
*interperts messages from our eyes into images we can understand.
Temporal Lobes
 * Process sound sensed by our ears.
* Process sound sensed by our ears.* Interpreted in audiory cortex
* NOT LATERALIZED
* Contains Wernike's Area: interprets written and spoken speech.
* Wernike's Aphasia: unable to understand language: the syntax and grammar jumbled.
Endocrine System
*System of glands that screte hormones.
*similar to nervous system except hormones work a lot slower than neurotansmitters.
Hypothalamus: (brain region controlling the pituitary gland)
Thyroid gland: affects metabolism among other things
Pituitary Gland: Secretes many different hormones, somes of which affects other gland
Parathyroids:(help regulate the level of calcium in the blood)
Adrenal Glands:( inner part called the medulla, helps trigger the "fight or flight" response
Pancreas: regulates the level of sugar in the blood
Testis: male sex hormones
Ovary: femal sex hormones


